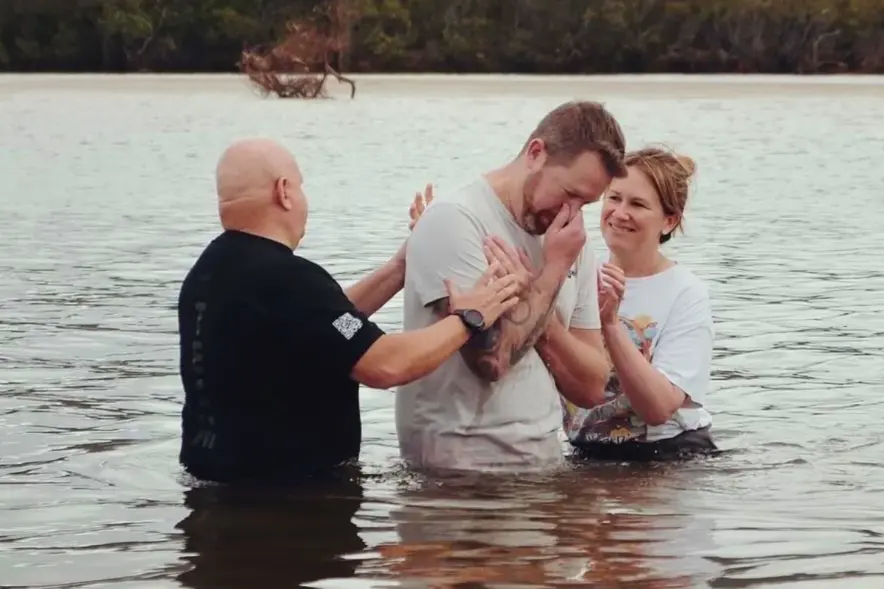
At the beginning of this year, I had the incredible privilege of baptising my brother, Brett, into the Christian...
Tag: church
Showed 1 to 9 posts out of 20 total under "Tag: church" category.
Women were active in the early church - prophesying, praying, teaching, and serving. Luke tells us of Anna...
“We are wounded in community and we are healed in community. No way around it. Healing might not come...
The Spark That Lit The Flame One of the contentious sparks that finally lit the flame we now know...
“And now, what are you waiting for? Get up, be baptised, and wash your sins away, calling on his...
If you’re an orthodox Christian, already familiar with the doctrine of the Trinity, you might like to head somewhere...
The ongoing conversation about the ‘role’ of women in the church, in marriage, and in society is not new....
New Testament holiness is a joyous privilege, not a heavy burden and duty.